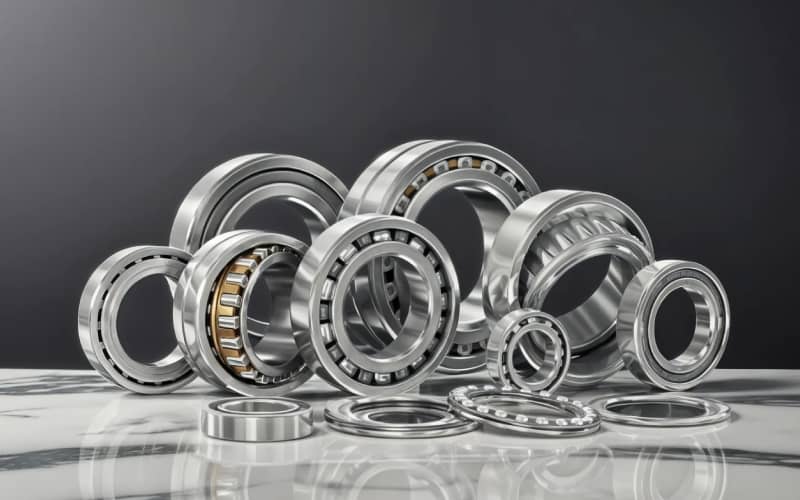
Choosing the right type of bearings is critical to the performance and longevity of machinery across various industries. From industrial equipment to everyday appliances, bearings play a critical role in reducing friction, supporting loads, and ensuring smooth motion.
However, selecting the wrong bearings or neglecting proper care can lead to premature failure, increased downtime, and higher costs.
This blog will explore the different types of bearings, how to select the right one for your needs, and practical tips to maximize their durability and performance.
Understanding the Importance of Choosing the Right Types of Bearing
Bearings are vital components in machinery operation, as they support moving parts and reduce friction between them. Choosing the right type of bearings impacts not only the efficiency of the machinery but also its operational lifespan. The wrong bearings type or incorrect installation can cause overheating, excessive wear, and ultimately lead to machine failure.
How Bearings Impact Machine Efficiency and Durability
Different bearings are designed for specific functions, load capacities, and environments. For instance, machines operating under heavy loads need bearings that can withstand stress without deforming or failing. Conversely, high-speed applications require bearings that generate minimal friction and heat.
Using the correct types of bearings ensures optimal machine efficiency, reducing energy consumption and wear on moving parts. This leads to longer machine life and fewer replacements or repairs.
Common Applications of Different Types of Bearings
Bearings are used in countless applications, from cars, airplanes, and construction machinery to household appliances and medical devices. Their versatility means that the wrong selection can have severe consequences. For instance, the bearings used in a high-speed electric motor are quite different from those found in a slow-turning conveyor system.
Key Types of Bearings and Their Unique Benefits
Selecting the right bearings depends on several factors, including the load, speed, and environmental conditions. Below are the most common types of bearings and their primary applications.
Ball Bearings: Versatile and Cost-effective
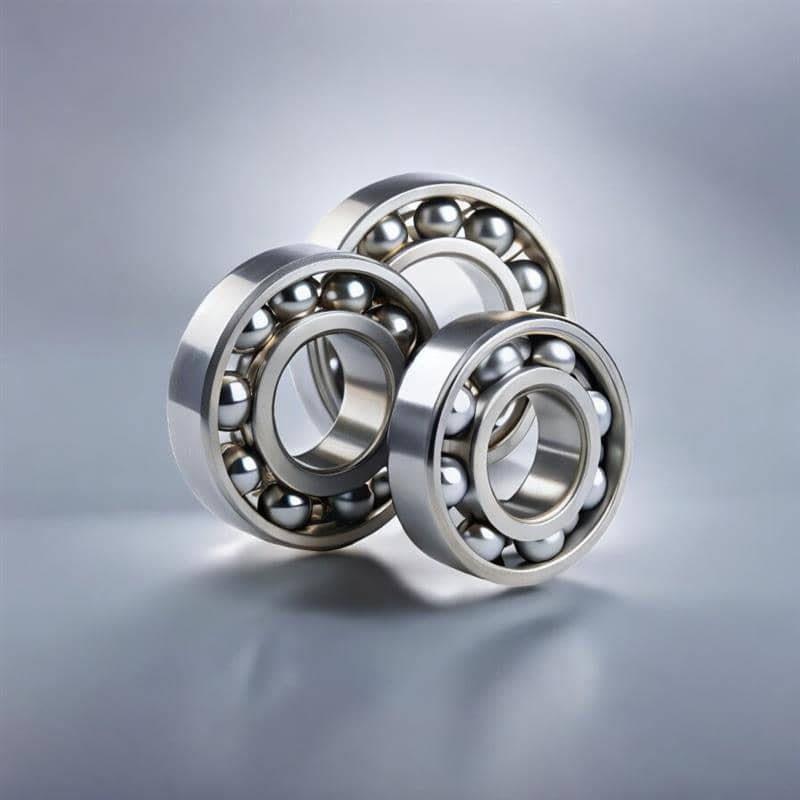

Ball bearings are among the most widely used type of bearings due to their simplicity and versatility. They are ideal for applications with relatively light loads and high speeds, such as electric motors and household appliances. Ball bearings can handle both radial and axial loads, but they are not well-suited for heavy-duty applications.
Roller Bearings: High Load Capacity for Industrial Applications
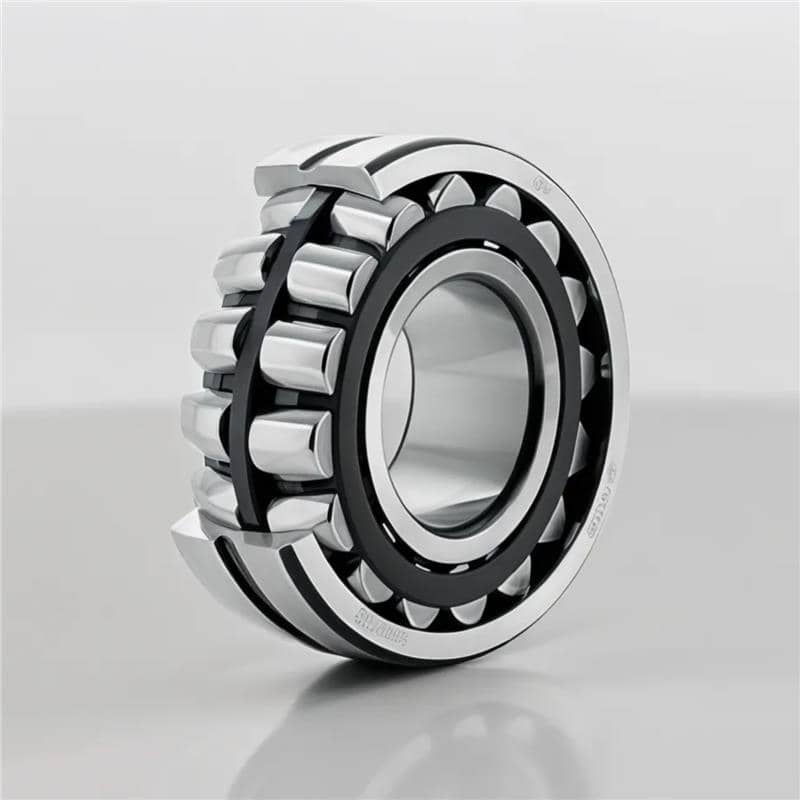

Roller bearings feature cylindrical rollers instead of balls, which increases their contact area and enables them to carry heavier loads. They are commonly used in industrial machinery like conveyor belts and gearboxes. Their high load capacity and ability to withstand shock loads make them ideal for heavy-duty applications.
Thrust Bearings: Handling Axial Loads Efficiently
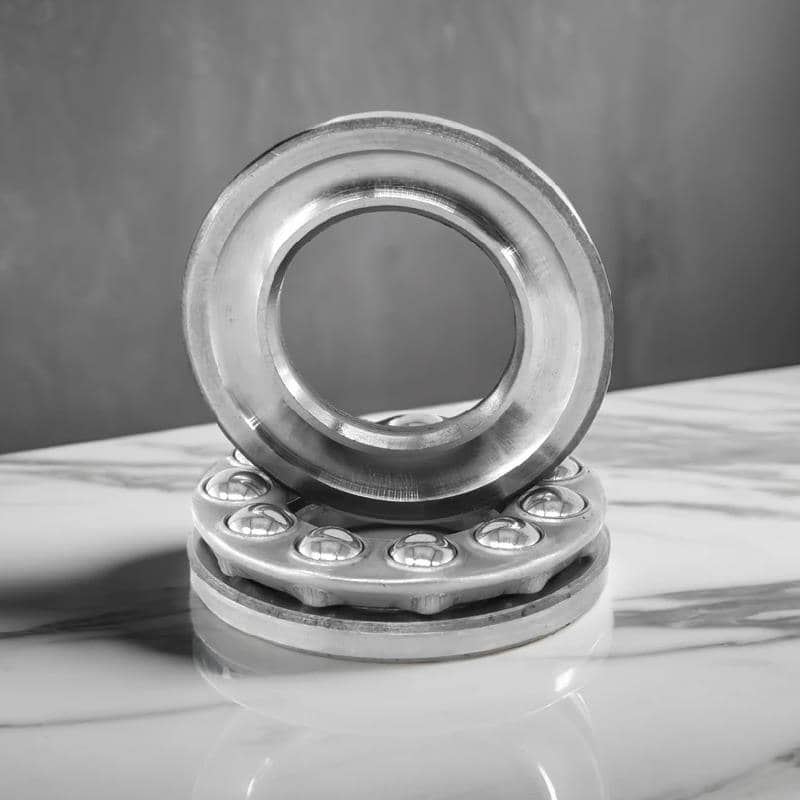

Thrust bearings are designed to manage axial loads, which are parallel to the bearing axis. They are commonly found in automotive and aerospace applications where axial thrust needs to be controlled. These bearings are not suitable for handling radial loads, so it’s important to use them in the correct applications.
Tapered Bearings: Balancing Radial and Axial Loads
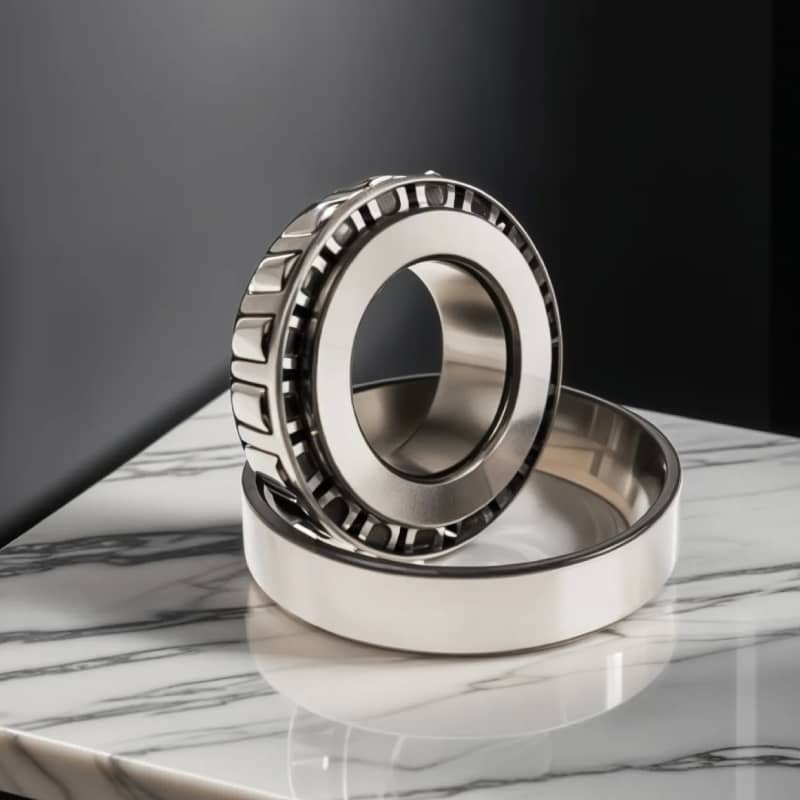

Tapered bearings are designed to handle both radial and axial loads simultaneously, thanks to their conical shape. They are often used in automotive hubs and heavy machinery, where a combination of forces is present. Their durability and load-bearing capacity make them highly efficient for rugged environments.
Needle Bearings: Compact and Lightweight for Limited Space
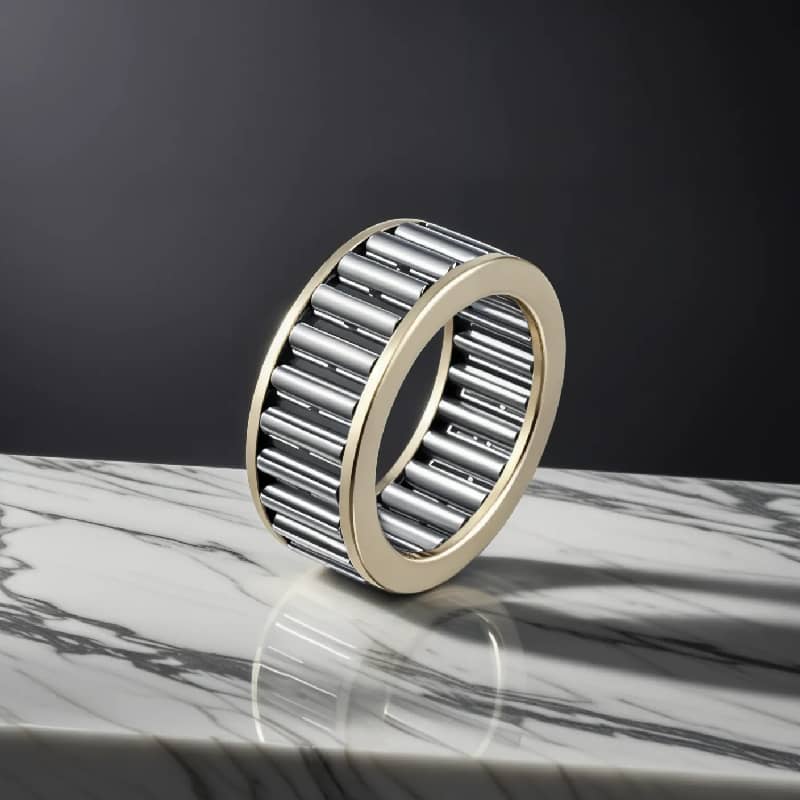

Needle bearings have long, thin rollers, which allow them to support high loads in a compact space. These bearings are ideal for applications where space is limited, such as in automotive transmissions. Their small size and ability to handle heavy radial loads make them valuable for high-load, low-speed environments.
Factors to Consider When Selecting the Right Type of Bearings
Choosing the appropriate bearings requires a clear understanding of the application’s operational demands. Below are the key factors to consider when selecting bearings.
Load Capacity: Matching the Bearings Type to the Application
Bearings are designed to support specific load types—radial, axial, or a combination of both. Ensure that the bearings you select can handle the loads encountered in your machinery. For instance, roller bearings are better suited for heavy radial loads, while thrust bearings are best for axial loads.
Rotational Speed: Ensuring Optimal Performance
Bearings must be able to rotate efficiently without generating excessive heat or friction. Ball bearings are often chosen for high-speed applications, whereas roller bearings are ideal for slower-moving, heavier loads. Matching the bearing type to the operating speed is crucial to prevent overheating and failure.
Operating Environment: Temperature, Moisture, and Dust Considerations
The working environment is a critical factor in bearings selection. For high-temperature or corrosive environments, such as those found in chemical plants or outdoor equipment, specialized bearings with heat-resistant or corrosion-resistant coatings may be necessary. In dirty or dusty environments, sealed bearings can prevent contamination and extend operational life.
Maintenance Needs: Lubrication and Care for Long-term Use
Different bearings require different levels of maintenance. Some, like sealed bearings, are virtually maintenance-free, while others require regular lubrication. Ensuring proper lubrication reduces friction and wear, extending the life of the bearings and preventing premature failure.
Practical Tips to Maximize the Durability and Performance of Bearings
Maximizing the durability and performance of your bearings involves more than just selecting the right type. Proper installation, regular maintenance, and early detection of wear can significantly extend bearings life.
Proper Installation Techniques
Incorrect installation is a leading cause of bearings failure. Bearings should be installed using the correct tools and procedures, avoiding excessive force or misalignment, which can lead to uneven wear or damage.
Routine Maintenance: Inspection and Lubrication
Regularly inspecting bearings for wear and tear is critical. Lubrication is essential to minimize friction, but it’s also important to use the correct type of lubricant for the specific bearings and operating conditions. Over-lubrication can be just as harmful as under-lubrication.
Identifying Early Signs of Bearings Wear and Failure
Listen for unusual noises, such as grinding or squealing, which can indicate bearings wear. Excessive vibration or heat is also a sign that the bearings may be nearing failure. By identifying these early warning signs, you can replace bearings before they cause damage to the machinery.
Ensuring Correct Bearings Alignment to Avoid Premature Failure
Misaligned bearings can break unevenly, leading to premature failure. Ensure that bearings are properly aligned with the shaft and housing to reduce stress and extend their lifespan.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using Different Types of Bearings
Even with the right selection of bearings, several common mistakes can reduce performance and durability. Here are a few to avoid:
- Overloading Bearings: Exceeding the load capacity of bearings will lead to failure. Always match the bearings to the load requirements of your application.
- Using the Wrong Lubricant: Incorrect or incompatible lubricants can cause bearings failure. Make sure to use the manufacturer-recommended lubricant.
- Neglecting Environmental Factors: Operating bearings in harsh conditions without proper protection can result in contamination and wear.
- Skipping Regular Maintenance: Bearings need routine care, including inspections and lubrication, to function optimally.
Future Trends in Bearings’ Technology
Advances in bearings are improving durability and performance. Two emerging trends include:
Hybrid Bearings for Enhanced Durability
Hybrid bearings, which combine ceramic and steel components, offer increased durability and resistance to corrosion, making them ideal for extreme environments.
Smart Bearings and Predictive Maintenance Systems
Smart bearings equipped with sensors can monitor performance in real-time, allowing for predictive maintenance. This technology helps prevent unexpected failures by providing early warnings when bearings need attention.
Conclusion: Achieving Long-term Performance with the Right Bearings Selection and Care
Selecting the correct types of bearings for your machinery is essential for maximizing both performance and durability. By considering load capacity, rotational speed, and environmental factors, and by following proper installation and maintenance practices, you can ensure long-lasting, efficient operation. Regular inspections and the right lubrication techniques will further extend the lifespan of your bearings, reducing downtime and increasing productivity.