Ball bearings are a crucial component in machinery, consisting of hard steel balls placed between two cylindrical rings. The inner ring is tightly connected to the axle, while the outer ring is closely aligned with the wheel. This design significantly reduces friction, as the smooth, lubricated balls roll effortlessly between the inner and outer surfaces. The fundamental principle behind ball bearings is that rolling objects encounter less friction than sliding ones. This concept is vital in reducing wear and tear in moving parts.
Why are Ball Bearings Needed for Reducing Friction in Machinery?

The need for ball bearings is constant in various industries because most machinery has mechanical components. They link stationary and moving components, minimizing friction-related issues. The effectiveness of these ball bearings in preventing friction damage, such as premature wear or failure of connected parts, is highly dependent on their quality.
Sourcing high-quality ball bearings from trusted partners like KG International is crucial. These bearings are designed to safeguard the moving parts of machinery from friction-induced damage, ensuring smoother operation and longer lifespan. The use of well-crafted ball bearings is a key factor in maintaining the efficiency and durability of mechanical systems, making them an indispensable element in various industrial applications.
Understanding Ball Bearings: A Brief Overview
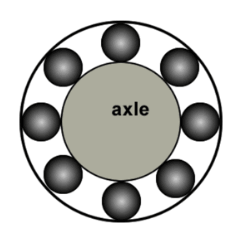
Ball bearings are essential components in various industrial applications, comprising a stationary outer casing and a rotating inner shaft. These elements are crucial for ensuring the smooth operation of numerous machinery and equipment.
Purchasing ball bearings, whether in the UAE or globally, necessitates a clear comprehension of their nature, operational mechanics, and the appropriate types for specific machinery.
Typically, a ball bearing includes five primary parts, each playing a vital role in ensuring seamless, low-friction interaction between two parts of a machine. This synergy is fundamental in maintaining the efficiency and longevity of the equipment in which it is used.
Function of Ball bearings
Reduction of Friction: Commonly misconceived as creating ‘frictionless resistance’, ball bearings reduce, rather than eliminate, friction. This misconception arises from overlooking the role of magnetic bearings, which is distinct from ball bearings. Ball bearings minimize friction between two surfaces, known as races. This reduction is vital as it stabilizes the races, lowers heat generation, reduces wear and tear, and diminishes the likelihood of part failure.
Linking Machine Parts: In any mechanical system, connecting different parts is necessary. Ball bearings fulfil this role by acting as joints. They are particularly useful in scenarios where one part rotates in relation to another, such as the connection between the fork and wheel of a bicycle. By using ball bearings, two components, often with different axes, are seamlessly integrated, ensuring smooth operation.
Load Bearing: The ability of a ball bearing to support weight depends on the width of its outer ring. Bearings are designed with a specific static load-bearing capacity, which influences their axial load limits. Some specialized bearings, like self-aligning bearings with double roll capacity, can handle heavier loads while maintaining durability. High-duty bearings can support loads up to 50% of their static load capacity, making them suitable for more strenuous applications.
Parts of Ball Bearings

Spherical Plain Bearings and Rod Ends are intricate mechanical components essential in various industrial applications. These bearings consist of several critical parts, each playing a vital role in their overall functionality and efficiency.
Steel Balls: These are the primary rolling elements. Steel balls are pivotal in the operation, facilitating smooth movement and reducing friction. They are positioned at the centre and enable the device to bear loads and rotate with minimal resistance.
The Cage: Cage is a crucial component designed to maintain an even distribution of the balls within the bearing. Crafted from materials that minimize friction, the cage ensures that the balls are evenly spaced, preventing contact and maintaining consistent performance.
The Inner Ring: This smaller ring serves as the foundation on which the steel balls rotate. In industrial settings, the inner ring is the part that moves, connected to the moving components. The inner ring, along with the outer ring, is designed with specific dimensions to accommodate the steel balls, with both rings sharing similar bandwidths but differing in diameter.
The Outer Ring: The outer ring, or outer race, is the larger counterpart to the inner ring. It forms the external boundary under which the steel balls operate. Unlike the inner ring, the outer ring usually remains stationary. Both rings feature grooves of varying depths, ensuring that the balls can roll smoothly and without deviation.
The Shield: An optional but highly recommended addition to the bearing is the shield. This component enhances the durability of a bearing by protecting the rolling elements from external contaminants like dust and moisture. Shields can be made from metal or plastic, with metal shields preventing dust accumulation and plastic ones offering increased resistance to water. Additionally, shields help in retaining lubricants like oil and grease, reducing maintenance needs, and prolonging the lifespan of a bearing.
These bearings require a specific radial and axial clearance for optimal performance. This clearance is crucial for accommodating thermal expansion during operation, which can result from residual friction. Proper clearance ensures that the bearings do not tighten excessively, wear prematurely, or seize, thus maintaining their efficiency and longevity.
Types of Bearings Offered by KG International
KG International offers a diverse range of bearings, each tailored to meet specific industrial needs. Understanding the right type of bearing for your machinery and operations is crucial, especially when selecting from a supplier in the UAE.
Firstly, radial bearings are engineered to endure forces that act perpendicular to the axis. They are essential for applications where such forces are predominant.
Next, axial bearings are unique in their design, trapping balls between races to resist axial forces effectively. This makes them suitable for scenarios where axial loads are a primary concern.
Angular contact bearings stand out by their ability to handle both perpendicular and axial loads simultaneously. This dual capacity makes them versatile for various mechanical applications.
Roller bearings are designed to reduce friction between moving parts significantly. They boast a higher load capacity than their ball-bearing counterparts, making them ideal for heavy-duty operations.
Linear bearings specialize in facilitating movement in a single direction, such as back-and-forth motions. This linear movement is crucial in many precision applications.
Self-aligning bearings are designed to accommodate the inclination of the axis. This is achieved through a double-roll bearing mechanism, ensuring smooth operation even when the axis is tilted.
Lastly, mounted bearings play a pivotal role in supporting rotating parts or in separating rotating components from stationary ones. This type of bearing is crucial in maintaining the stability and efficiency of various mechanical systems.
Each bearing from KG International meets specific mechanical demands, ensuring optimal performance in diverse industrial applications.

